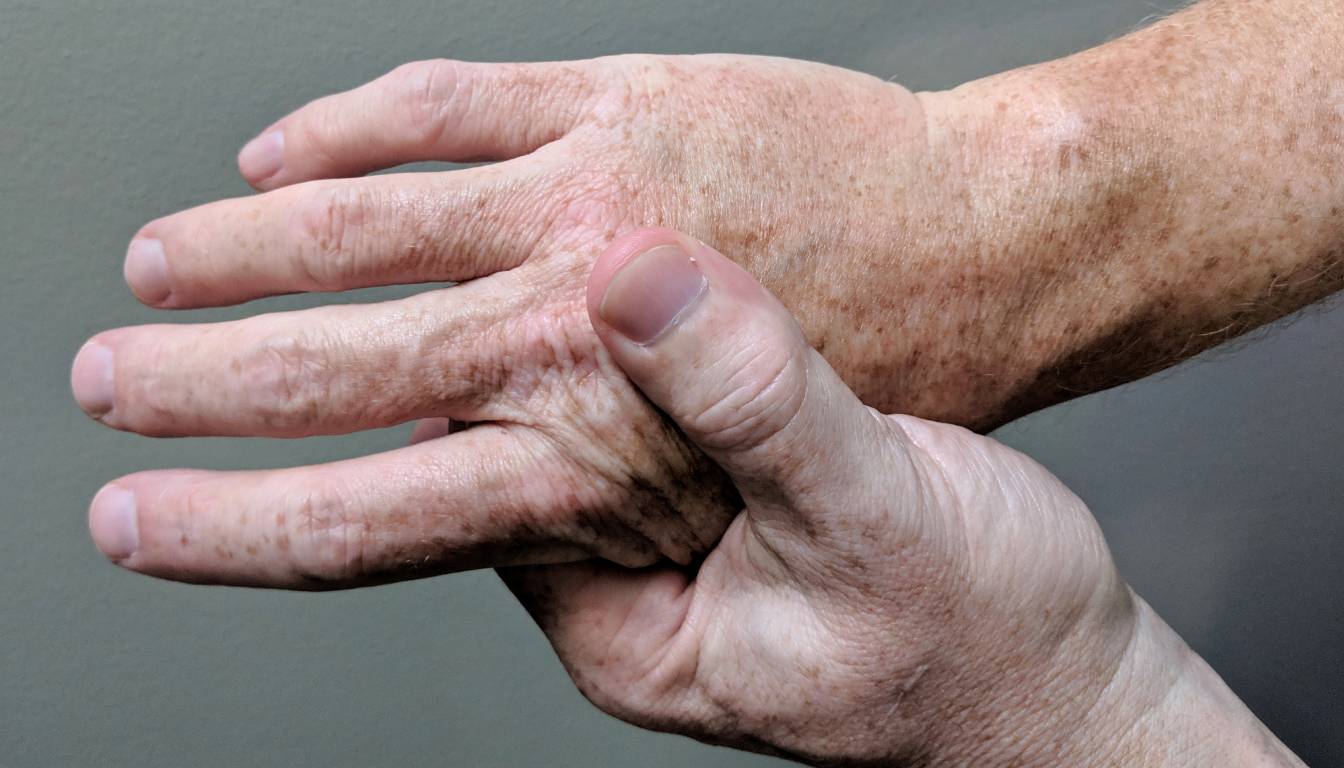
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can feel like an uphill battle. Every day brings the challenge of managing pain and stiffness while trying to maintain a sense of normalcy. I know how overwhelming it can be to navigate a world that often feels unyielding, but understanding this condition is the first step toward reclaiming your life.
Rheumatoid arthritis isn’t just a physical ailment; it’s a complex autoimmune disorder that affects millions. The good news is that with the right knowledge and strategies, you can take control of your health. Join me as we explore effective management techniques, the latest treatments, and inspiring stories that highlight resilience in the face of adversity. Together, we can turn the tide on rheumatoid arthritis and embrace a brighter, more active future.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis affects many people, leading to pain and stiffness. I find understanding this condition crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder. In this condition, the immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation. This reaction can lead to joint damage over time. It’s important to know that it can affect other body parts, not just the joints. Individuals may experience fatigue and fever, along with joint issues.
Common Symptoms and Signs
Some common symptoms include joint pain and swelling. Stiffness often happens, especially in the morning. I’ve noticed some friends mention fatigue that seems to linger. People with rheumatoid arthritis might also suffer from loss of appetite and occasional fevers. Recognizing these signs is key to seeking prompt treatment and improving daily life.
Understanding these aspects can help those affected lead more fulfilling lives despite their challenges.
Causes and Risk Factors
Rheumatoid arthritis arises from several causes and risk factors that shape its development. Understanding them can help me take proactive steps.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in rheumatoid arthritis. Specific genes increase the likelihood of developing this condition. If a family member has it, my risk goes up. Researchers identified the HLA-DR4 gene as a strong contributor. However, not everyone with this gene develops the disease. Genetic predisposition combined with environmental triggers often determines outcomes.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers can also trigger rheumatoid arthritis. Factors like smoking increase inflammation and worsen symptoms. Exposure to certain infections may initiate the immune response that leads to the disease. Additionally, factors like obesity contribute to joint stress, making my situation worse. Staying aware of these triggers helps me manage my health more effectively and avoid potential pitfalls.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis involves multiple steps. Healthcare providers gather key information through medical history and physical examinations.
Medical History and Physical Exam
During the medical history, doctors ask about symptoms like joint pain, swelling, and fatigue. I share details about my family history with rheumatoid arthritis. This information helps pinpoint potential genetic links. In the physical exam, doctors check joint tenderness and range of motion. They look for swelling, warmth, and signs of inflammation. A thorough exam reveals important clues about my condition.
Diagnostic Tests
Doctors often recommend blood tests to evaluate specific markers. Tests like the rheumatoid factor or anti-CCP antibodies help confirm a diagnosis. Joint X-rays may be necessary to spot any damage. Sometimes, ultrasound or MRI is used to get a closer look at joint health. The results from these tests guide treatment decisions, providing clarity about the condition. Getting these tests can feel like a chore, but they play a crucial role in my journey with rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment Options

When managing rheumatoid arthritis, multiple treatment options help improve quality of life. I focus on medications and lifestyle changes to ease symptoms and boost overall well-being.
Medications
Medication plays a key role in managing symptoms. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly prescribed. These work by slowing disease progression and reducing joint damage. Methotrexate is a popular choice among DMARDs. It’s effective but may require regular blood tests to monitor effects. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help relieve pain and inflammation. Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen work well for many. If symptoms become more severe, biologics might be necessary. These are advanced medications that target specific parts of the immune system. I find it crucial to discuss all options with a healthcare provider, as they can recommend the best fit based on individual needs.
Lifestyle Changes
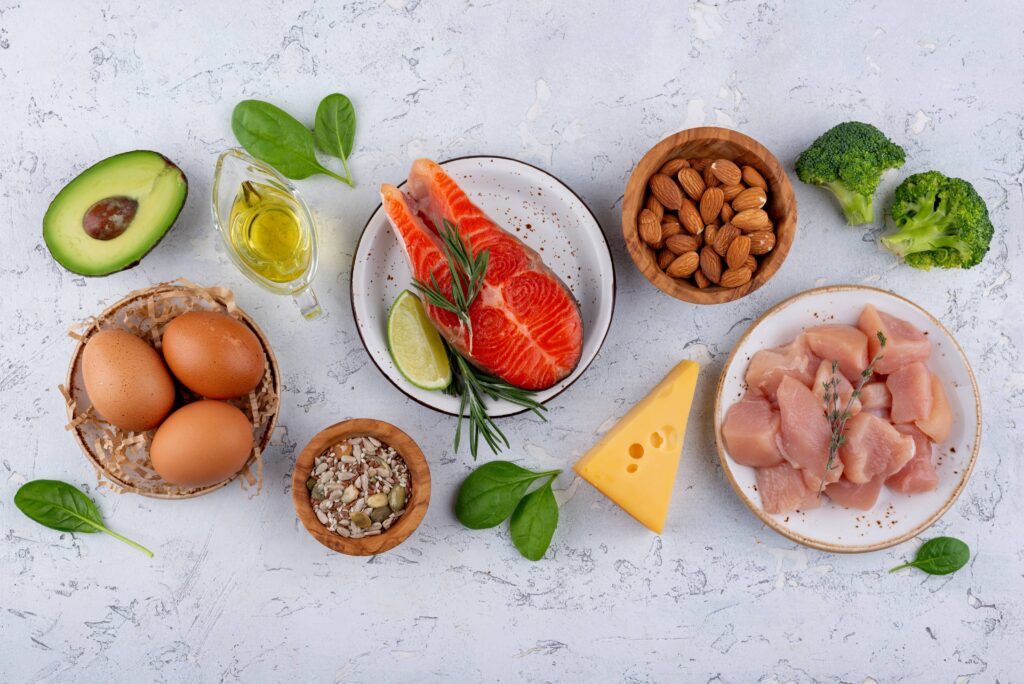
Simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference. I emphasize regular exercise as a game-changer. Low-impact activities such as swimming or walking keep joints flexible and strengthen muscles. Nutrition matters too. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids reduces inflammation. I enjoy incorporating these foods into meals, making it easier to stay on track. Stress management is another important area. Mindfulness and yoga help maintain mental clarity and relax the body. Lastly, quality sleep can’t be overlooked. A good night’s rest restores energy and supports overall health. Implementing these changes might just elevate my daily routine and boost my well-being.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with rheumatoid arthritis offers challenges every day. I experience pain and stiffness that can make even simple tasks feel like a marathon. Still, I embrace strategies and support that help me manage my symptoms and lead a fulfilling life.
Coping Strategies
Coping with rheumatoid arthritis requires a proactive approach. I find that consistency matters. Regular exercise helps keep my joints flexible. Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling are gentle yet effective. Balance is key in every aspect of life. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains boosts my energy while lowering inflammation.
Mindfulness practices also help me stay grounded. I dedicate time each day to meditation or deep breathing. Stress management becomes easier when I prioritize mental health. Connecting with others facing similar challenges provides comfort. Sharing experiences often leads to valuable tips that can make life feel lighter.
Keeping a daily journal helps me track my symptoms and identify triggers. Celebrating small victories keeps my spirits high. When I have a good day, I embrace it fully.
Support and Resources
Support is critical in managing rheumatoid arthritis. I lean on my healthcare team for guidance. Regular check-ins keep me informed about new treatments and strategies. Online support groups provide a sense of community. Sharing stories and advice helps me feel less alone.
Local organizations often offer resources and workshops. They teach skills that improve my daily life. Attending these sessions can be a game changer. I gather useful information and meet new friends at the same time.
Books and websites dedicated to rheumatoid arthritis keep me educated. I ensure I follow credible sources to stay informed about the latest research. Knowledge empowers me to advocate for myself effectively.
Before You Go – Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be a daunting journey filled with ups and downs. However, I’ve learned that taking control of my health through informed choices can make a significant difference. By understanding my condition and exploring various treatment options I can manage symptoms more effectively.
It’s essential to stay proactive and seek support from healthcare professionals and communities. Embracing lifestyle changes and coping strategies has empowered me to face each day with resilience. I hope my insights inspire others to reclaim their lives and find their path to wellness. Don’t forget to add The Herb Prof to your favorites so you don’t miss out on future articles.
References – Rheumatoid Arthritis
Little Herb Encyclopedia, by Jack Ritchason; N.D., Woodland Publishing Incorporated, 1995
The Ultimate Healing System, Course Manual, Copyright 1985, Don Lepore
Planetary Herbology, Michael Tierra, C.A., N.D., Lotus Press, 1988
Handbook of Medicinal Herbs, by James A. Duke, Pub. CRP Second Edition 2007
The Complete Medicinal Herbal, by Penelope Ody, Published by Dorling Kindersley
Before You Go – Check the Following Articles!
Aging Prematurely: How To Reverse It!
Free Healing Herbal Remedy for Bursitis Swelling
Check these Categories:
Frequently Asked Questions – Rheumatoid Arthritis
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and potentially joint damage. It affects daily life, leading to symptoms like joint stiffness, swelling, and fatigue.
What are the common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include joint pain, swelling, morning stiffness, fatigue, loss of appetite, and occasional fevers. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment and improved quality of life.
What causes rheumatoid arthritis?
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, but genetic factors play a significant role. Environmental triggers, such as smoking, specific infections, and obesity, can also contribute to its development. A family history may increase the risk but is not definitive.
How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers look for symptoms and may use blood tests, X-rays, or imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI to verify the condition.
What treatment options are available for rheumatoid arthritis?
Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief, and biologics for severe cases. A balanced lifestyle including exercise, diet, and stress management is also emphasized.
How can lifestyle changes impact rheumatoid arthritis?
Lifestyle changes can significantly improve the quality of life for those with rheumatoid arthritis. Regular low-impact exercise, a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, proper sleep, and stress management techniques like mindfulness can help manage symptoms effectively.
What coping strategies are recommended for dealing with rheumatoid arthritis?
Coping strategies include maintaining a daily journal to track symptoms and triggers, celebrating small victories, engaging in regular exercise, and seeking support from healthcare teams and online communities. Staying informed empowers patients to advocate for their health.
Is there a support community for people with rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, there are many online communities and local organizations dedicated to supporting individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. These platforms provide valuable resources, shared experiences, and a sense of community to help manage the challenges of the condition.